CCL4 Liver Fibrosis Model
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
The two most commonly used animal models of liver fibrosis are induced chemically (carbon tetrachloride; CCl4) or by bile duct ligation (BDL). CCl4 causes hepatocyte damage, necrosis, inflammation, and fibrosis after 4 weeks of challenge and over 8 weeks causes cirrhosis. In contrast, BDL stimulates the proliferation of biliary epithelial cells and oval cells causing proliferating bile ductules with accompanying portal inflammation and fibrosis.
Liver fibrosis is a wound healing response to acute or chronic injury that results in the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, i.e., scar tissue. Advanced liver fibrosis results in cirrhosis, liver failure, and portal hypertension.
In animal models of liver fibrosis, the insult induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) resembles important properties of human liver fibrosis including inflammation, regeneration, and fiber formation. This model is commonly used to study acute liver injury, advanced fibrosis, as well as fibrosis reversal. Additionally, the CCl4 induced liver fibrosis model is highly reproducible and therefore an excellent candidate for drug screening.
The study summarized below illustrates the profound fibrotic phenotype of the CCl4 model. There is currently no approved therapeutic for treating this condition and accordingly no positive control for validating the model. Nonetheless it is an accepted essential model for evaluating anti-fibrotic candidate therapeutics.
Ready to get started or looking for a custom model?
Contact us today for more information about our bespoke research models and to discuss how we can help you answer your unique research questions.
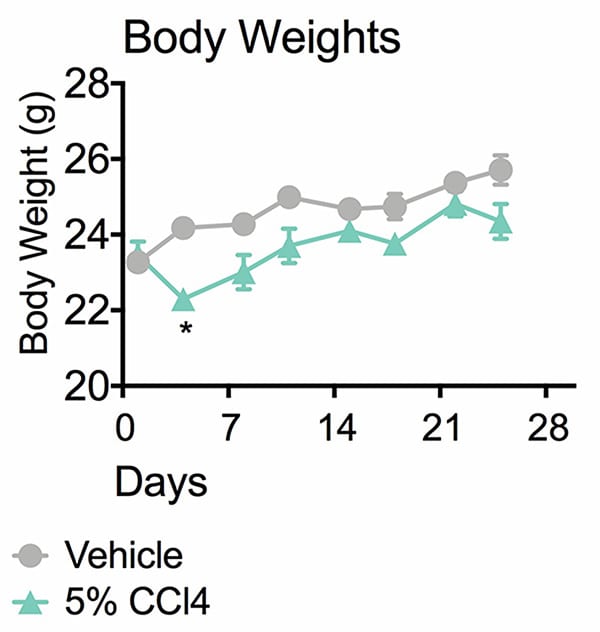
Body Weights. This study was conducted in male Balb/c mice (N=10). After the first two doses, animals receiving 5% CCl4 had a significant drop in body weight at day 4. Though these animals continued to grow, they remained 2-5% smaller than their vehicle counterparts. Data are mean ± SEM; *p<0.05 compared to vehicle control.
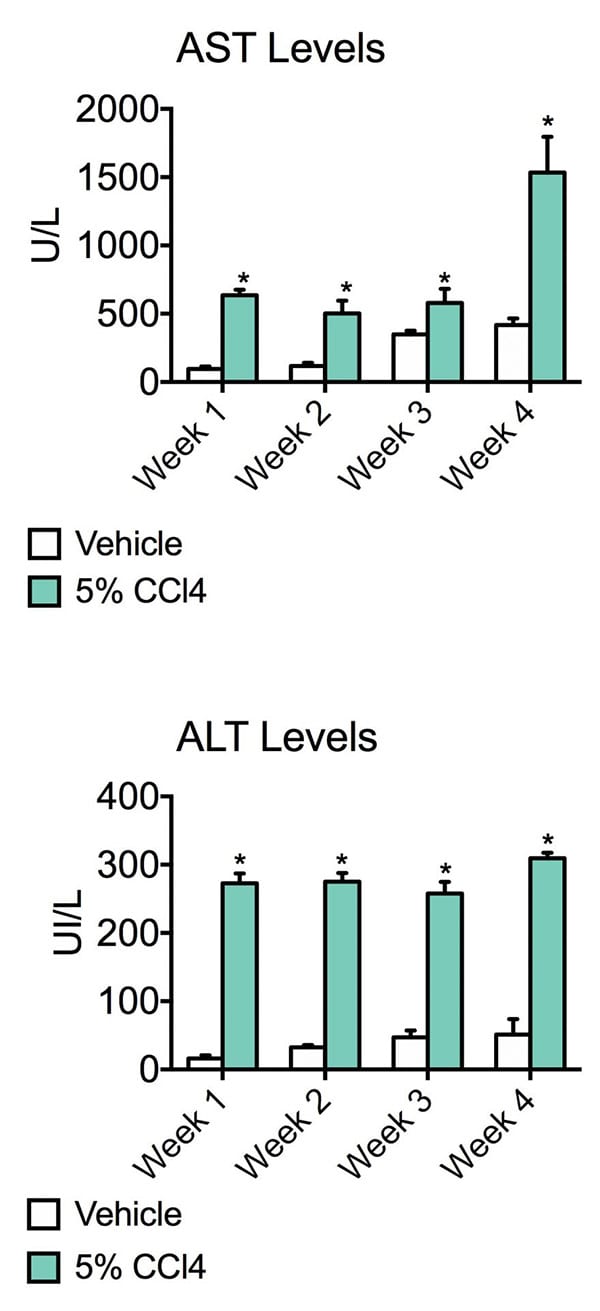
AST levels and ALT levels. Aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) are commonly measured clinical biomarkers of liver health. Both AST and ALT levels were significantly elevated in CCl4 administered animals for the entire duration of the study, suggesting that liver damage has occurred. Data are mean ± SEM; *p<0.05 compared to vehicle control.
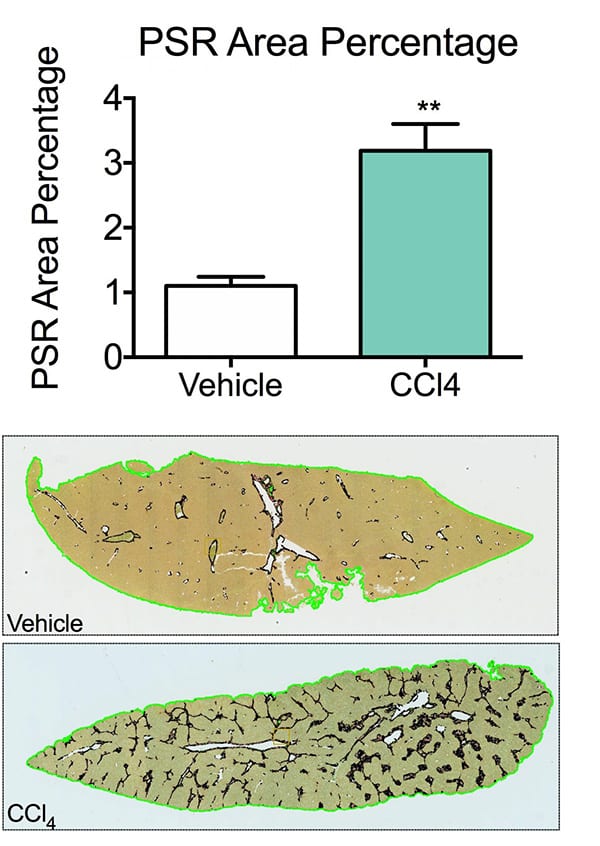
PSR Area Percentage and Staining. Picrosirius Red (PSR) staining is a commonly used histopathology technique to visualize collagen/fibrosis in tissue sections. The percentage of PSR detected in liver sections from animals receiving CCl4 was significantly higher than that of vehicle animals, suggesting that fibrosis has been achieved. Sections of liver were also scored for pathology (0= no finding, 1= minimal, 2= mild, 3= moderate, 4= marked, 5= severe). Data are mean ± SEM; **p<0.01 compared to vehicle control.
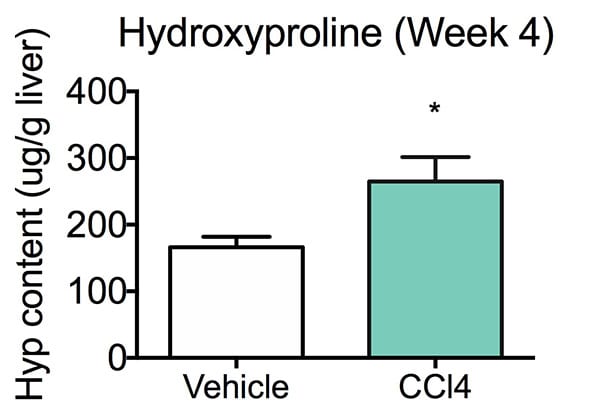
Hydroxyproline Content(week4). Hydroxyproline (4-hydroxyproline, Hyp) is a common non proteinogenic amino acid. Hydroxyproline in tissue hydrolysates is an indirect measure of the amount of collagen deposition. In line with the results of PSR collagen staining, hepatic Hyp content levels in CCl4 treated animals were significantly higher than vehicle treated animals. Data are mean ± SEM; *p<0.05 compared to vehicle control.
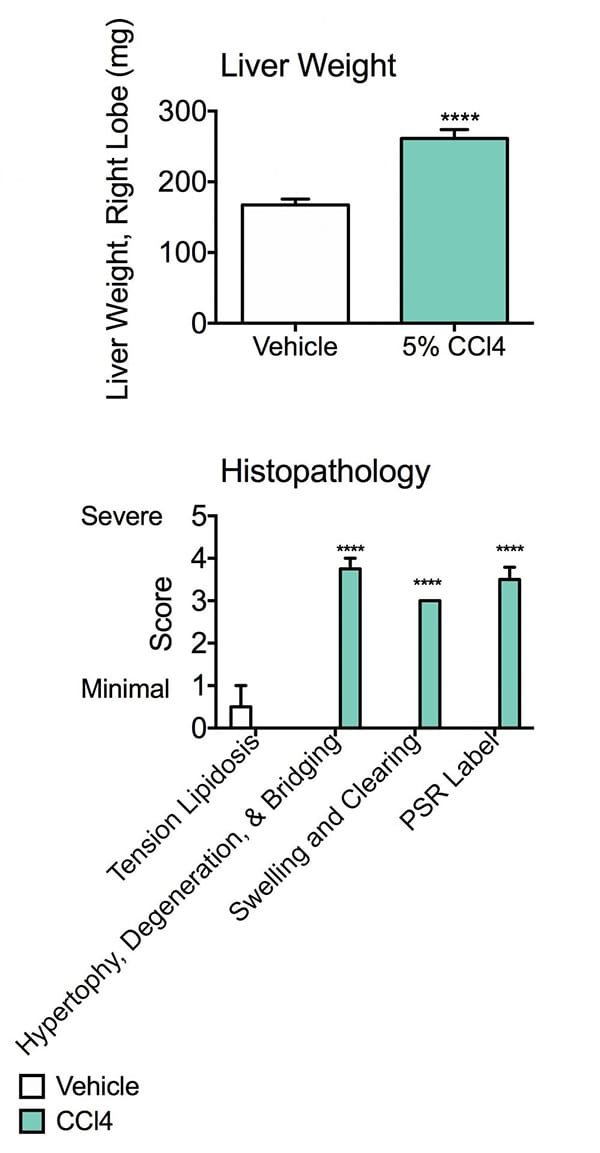
Liver weight and Histopathology. The right lobe of the liver was weighed prior to homogenization; livers of the CCl4 group were significantly heavier than those of vehicle animals. This may be related to hypertrophy and increased swelling found in the pathological analysis. Data are mean ± SEM; ****p<0.0001 compared to vehicle control.
These data illustrate the clinically relevant presentation of liver fibrosis in this animal model. The features described above are highly reminiscent of those seen in human liver fibrosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Liver enzyme levels (AST, ALT) can be measured and is increased in this liver fibrosis model. Hydroxyproline content within the liver can be measured and is increased in this liver fibrosis. However, histology is one of the most accurate ways of observing liver fibrosis.
We have relationships with a few histology labs that are able to perform all the histology tissue processing and analysis if requested.
Synonyms: Hepatic, Cirrhosis