Ex Vivo Liver Fibrosis Model
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
The ex vivo liver fibrosis model combines Melior’s CCl4 liver fibrosis model with Visikol’s precision cut tissue slicing capability’s. Our two companies have collaborated and validated this model to provide the benefits of intact in vivo tissue composition and its inherent face validity as an experimental system with the throughput provided by tissue culture format. This model is ideally suited for screening large numbers of compounds for their effects on gene expression associated with liver fibrosis.
In this model, liver fibrosis is induced with administration of CCl4 using the same protocols as Melior’s standard CCl4model. At an intermediate time-point, when tissue damage is well established and fibrosis is just initiating (customarily around 2 weeks) animals are sacrificed and livers presented to Visikol for precision slicing and subsequent tissue culture. Slices are typically maintained for 72 hours with test article treatment where upon gene expression is monitored by rtPCR and / or immunohistochemistry.
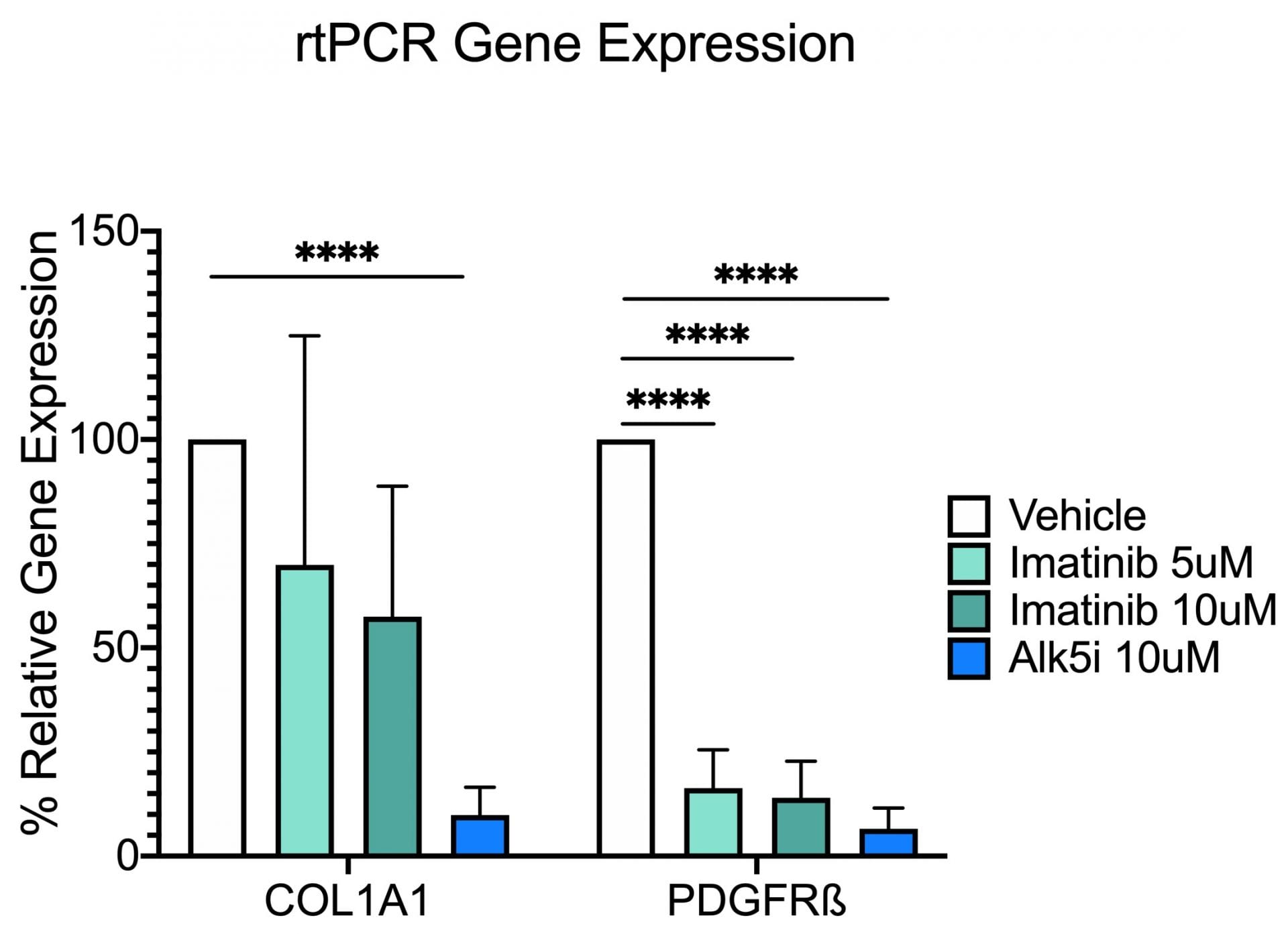
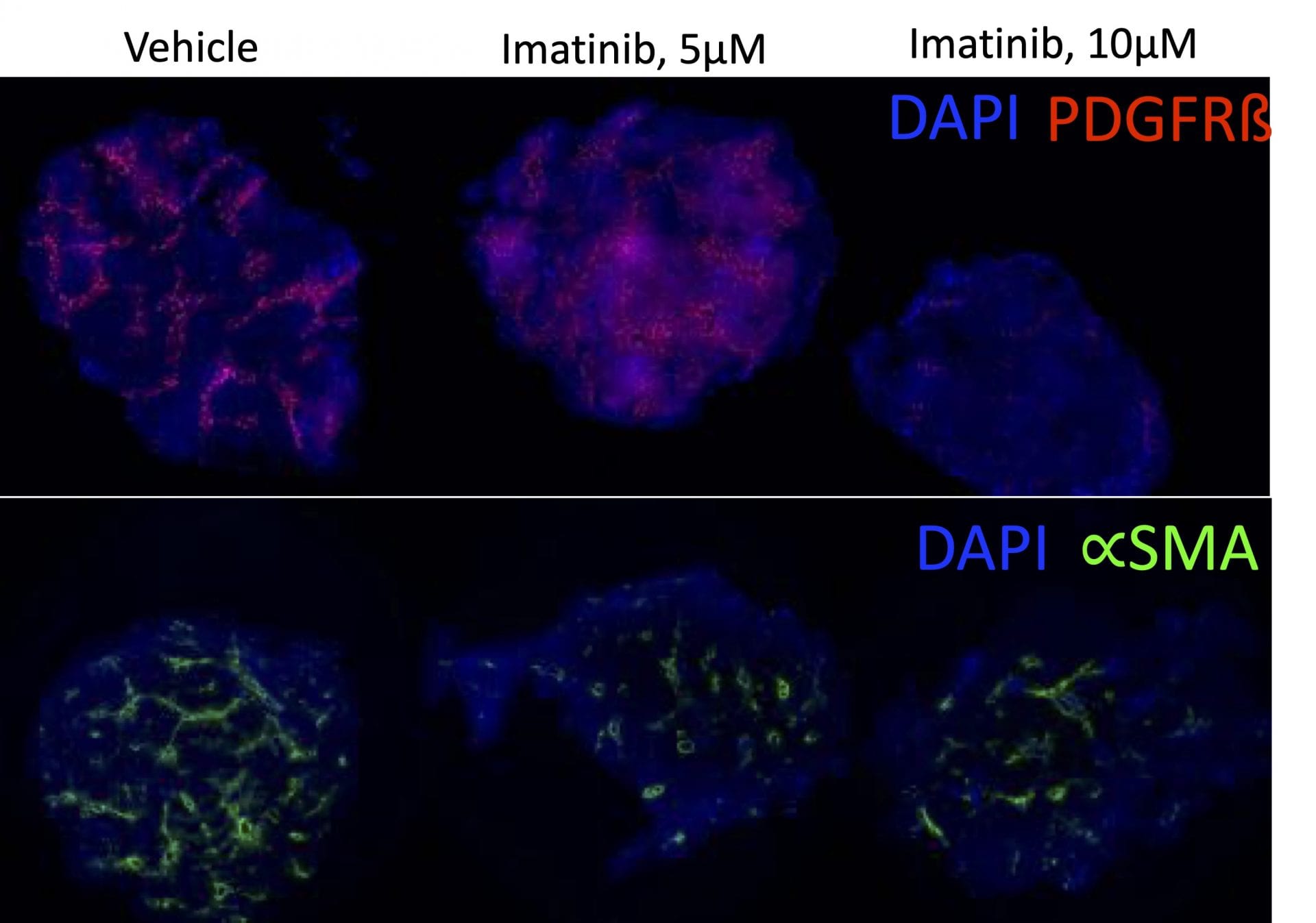
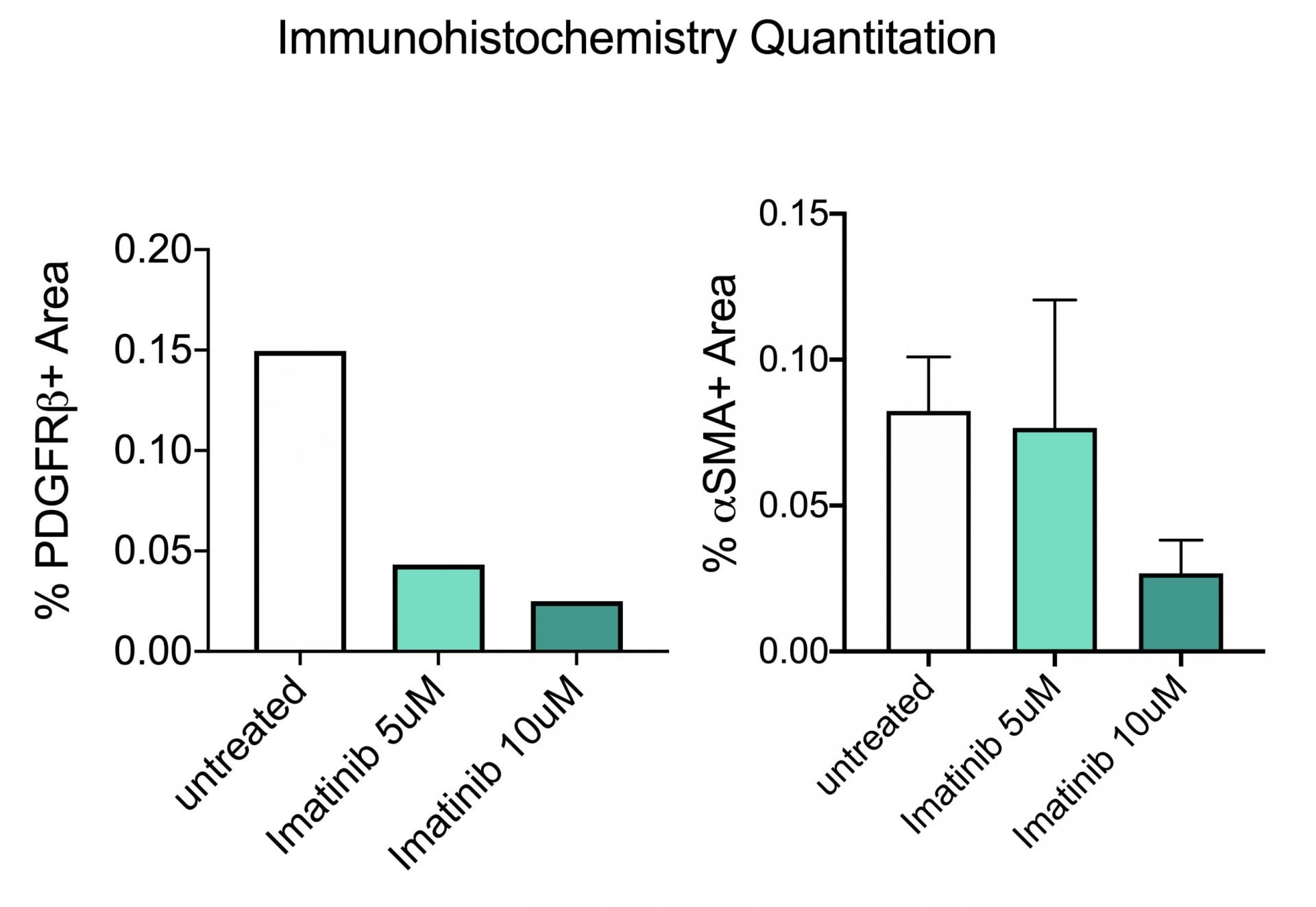
In the study illustrated below, the inhibition of markers of fibrosis including collagen and the platelet derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) are inhibited by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (Gleevac®) or with an inhibitor of transforming growth factor ß receptor (ALK5). The study further illustrates that immunohistochemistry can be used to quantitate expression levels as demonstrated by the inhibition of PDGFR and ∝-smooth muscle actin (∝-SMA) upon imatinib treatment.
Collagen 1A1 and PDGF Receptor ß Gene Expression. This study was conducted in male C57BL/6 mice (N=6). Livers were harvested and transferred to Visikol’s facility on wet ice. Precision cut tissue slices were made the same day and cultured for 72 hours under different treatments with replicates (n=3) for each treatment group. After 72 hours tissue was harvested from culture wells and processed for rtPCR analysis. Data are mean ± SEM; ****p<0.0001 compared to vehicle control (n=3)
Immunohistochemistry. This study was conducted in male C57BL/6 mice (N=6). Livers were harvested and transferred to Visikol’s facility on wet ice. Precision cut tissue slices were made the same day and cultured for 72 hours under different treatments with replicates for each treatment group. After 72 hours tissue was harvested from culture wells and processed for immunohistochemistry analysis.
These data illustrate the versatility of this in vivo / ex vivo hybrid model. Its most advantageous features are the number of compounds that can be screened across a diverse array of biomarkers while largely maintaining the tissue integrity of intact liver and crucial microenvironment of different liver cell types.

 Interested in running an Ex Vivo Liver Fibrosis study?
Interested in running an Ex Vivo Liver Fibrosis study?