Pulmonary Allergic Asthma
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
Allergic asthma is a condition that is initiated by an immune response to a diverse array of allergens and is manifested by airway obstruction, hyper-reactivity, and lung inflammation. This asthmatic response can be mimicked in experimental animal models of asthma by sensitizing and then exposing them to an array of antigens.
Like the asthmatic response in humans, the animal asthma model of pulmonary inflammation is characterized by an extensive inflammatory response including an influx of leukocytes such as monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1). This inflammatory response can be attenuated by administration of a number of known anti-inflammatory agents.
In this asthma mouse model we have initiated pulmonary inflammation using ovalbumin as the antigen and evaluated the effects of a well-known steroidal anti-inflammatory, dexamethasone, on the production of the inflammatory chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)
Ready to get started or looking for a custom model?
Contact us today for more information about our bespoke research models and to discuss how we can help you answer your unique research questions.
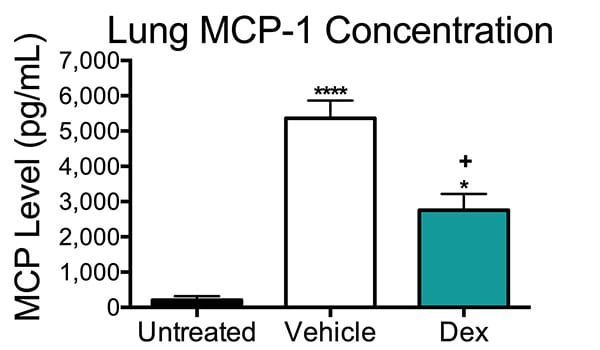
To induce allergic sensitization, mice were injected twice IP with 0.2 ml of 0.5 mg/ml ovalbumin on days 1 and 7. On days 22, 23 and 24 ovalbumin was administered intranasally into anaesthetized mice. For the dexamethasone-treated group, dexamethasone was administered orally 30 min prior to each intranasal exposure and on the day of dissection. On day 25 mice were euthanized and lungs removed and analyzed for MCP-1 levels.
Administration of dexamethasone significantly attenuated the inflammation response so that, while MCP-1 levels were higher than untreated animals, they were significantly lower than vehicle-treated animals. Data are mean ± SEM; *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001 (compared to untreated animals);+ p<0.05 (compared to vehicle-treated animals (N=6-8)).
This asthma animal model is normally configured as a 4 week or 1 month study. Test articles are typically administered in repeat fashion. Groups sizes of 6 to 10 animals are normally used depending upon the expected effect size of the test article.
Frequently Asked Questions
This asthma model is normally configured as a 4-week study. Test articles are typically administered in a repeat fashion.
Absolutely! Make sure to talk to our scientist to make sure your cytokine of interest plays a role in this model.
Synonyms: Asthmatic, pulmonary inflammation
