Folic Acid Kidney Fibrosis Model
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
Chronic kidney diseases result from recurrent or progressive injuries in glomeruli, tubules, interstitium and/or vasculature. In order to study pathogenesis, mechanisms and effects of interventions, many animal models have been developed, including spontaneous, genetic and induced models. We have established a folic acid nephropathy model. In this model, folic acid induces interstitial kidney fibrosis. High dosages of folic acid (250µg/g BW) given IP in mice induces folic acid crystals rapidly with tubular necrosis in the acute phase (1–14 days) and patchy interstitial fibrosis. Folic acid renal injury is induced both by crystal obstruction and direct toxic effect to tubular epithelial cells.
Kidney Fibrosis model data: Plasma concentrations of BUN and creatinine in mice injected with 250 mg/kg of folic acid (FA) and sacrificed 7 and 14 days (7D and 14D) post-injection. Plasma samples were used for blood nitrogen urea (BUN) and creatinine measurements with Alfa Wassermann Vet ACE Axcel® Chemistry System, according to manufacturer’s protocol. ***P<0.0001, ***P<0.001, one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Fisher’s LSD test, n=6-8/group.
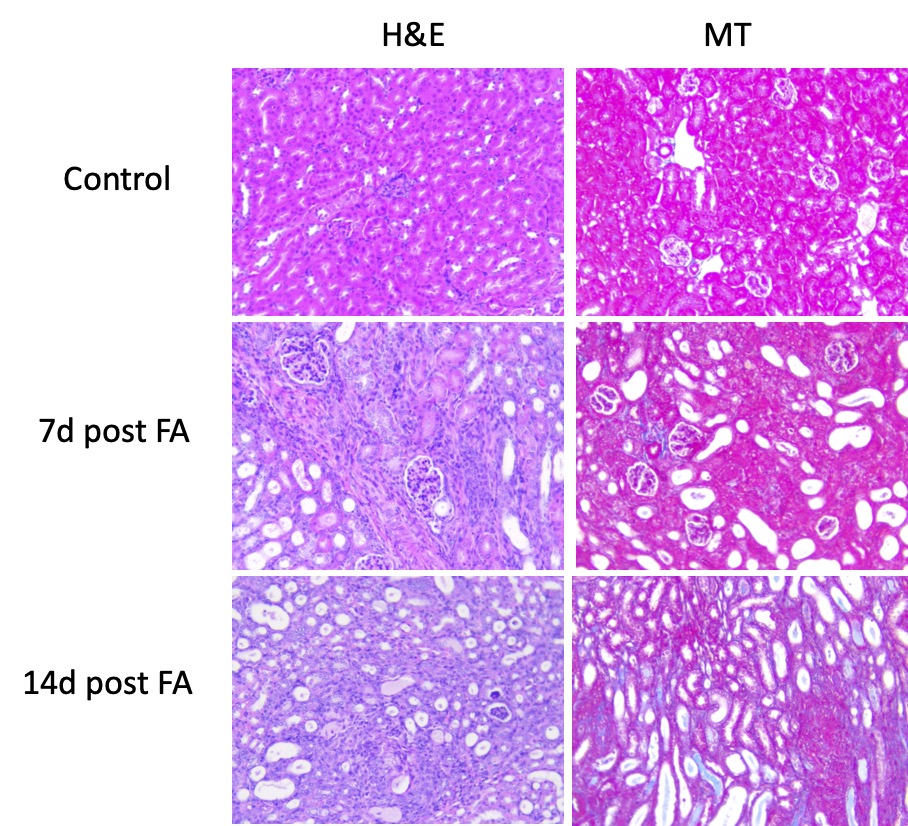
Representative histological images of formalin-fixed kidney tissue processed for H&E and Masson Trichrome (MT) staining. Animals were treated with vehicle or folic acid and sacrificed 7 and 14 days after the treatment.
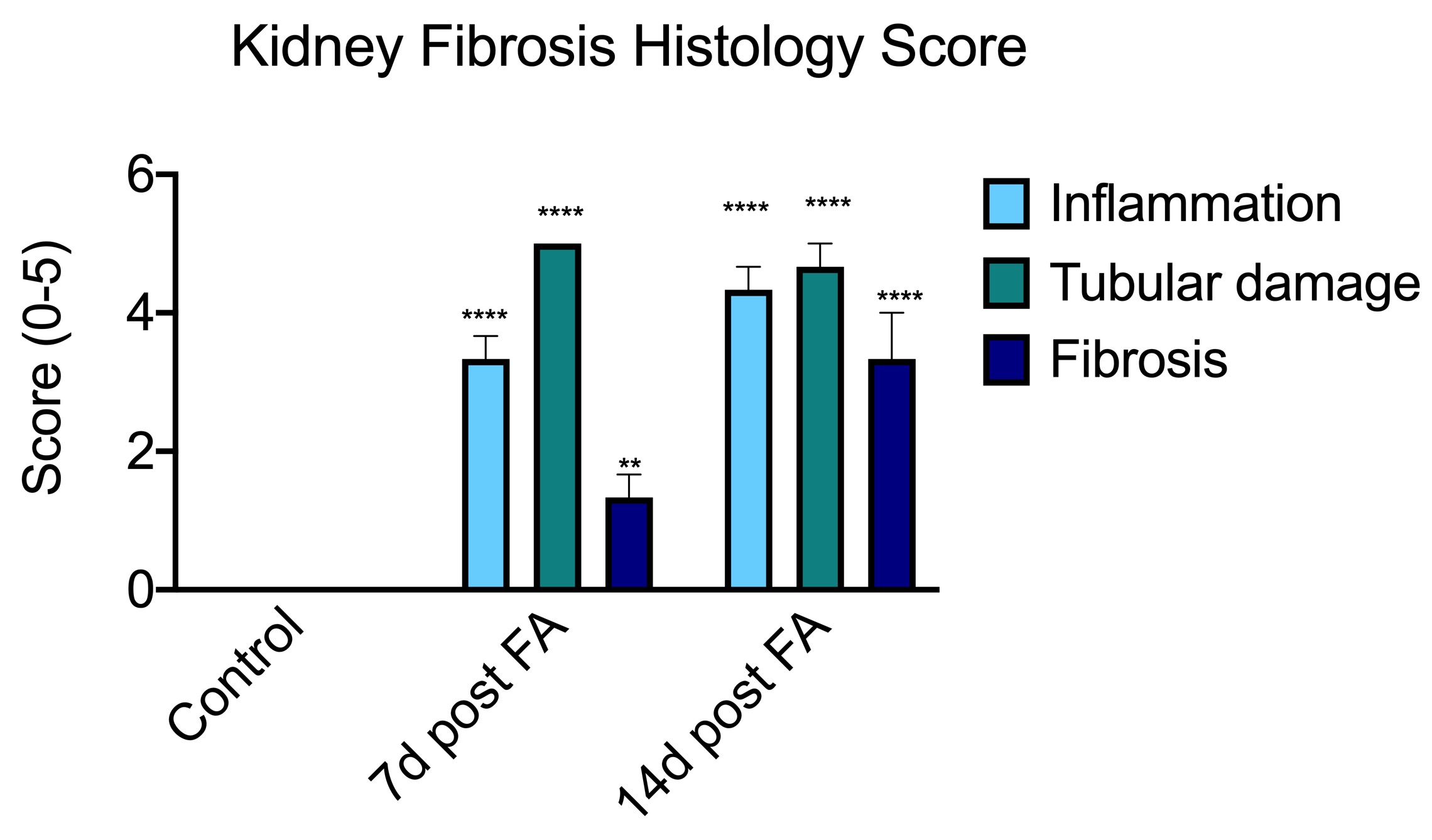
Pathological evaluation and scoring of inflammation, tubular damage and fibrosis by a veterinary pathologist blinded to treatments. Processed slides were scored from 0 to 5 for each measure. Control (vehicle-treated) kidneys were considered normal (score 0). Scores from 3 animals foreach treatment were analyzed by a non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test. ****P<0.00001, **P<0.01, n=3/group.
The folic acid-induced kidney fibrosis model can be run in either rats or mice. Typical protocol lengths are 14 days. In addition to the markers of kidney damage shown above, studies also typically involve histology and/or hydroxyproline as a biomarker of kidney fibrosis.