Maximal Electroshock (MES)
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
Epilepsy is a significant medical problem facing millions of people, most of who are not controlled by the current anticonvulsants on the market. Although several marketed anticonvulsants exist there remains a significant unmet medical need for better anticonvulsants with reduced liability.
Amongst all animal models of seizure and epilepsy, the maximal electroshock (MES) model is categorized as a model of generalized tonic-clonic seizure. When screening anticonvulsant candidates the MES model is an excellent tool for evaluating anti-seizure characteristics compared to a focal or partial seizure model (Psychomotor Seizure) such as the 6 Hz Model.
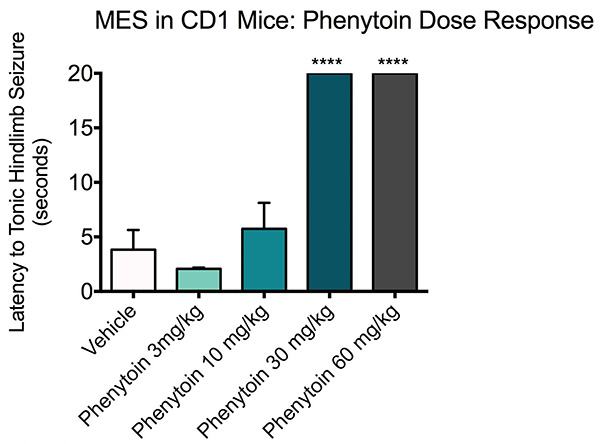
In the study described below, the effects of Phenytoin at various dose levels of 3, 10, 30 and 60 mg/kg were compared to vehicle treated mice. Animals were treated with either vehicle or Phenytoin and observed for 60 minutes prior to MES.
Ready to get started or looking for a custom model?
Contact us today for more information about our bespoke research models and to discuss how we can help you answer your unique research questions.
Maximal electroshock Phenytoin dose response. ICR-CD-1 mice (N=10) were treated with vehicle or Phenytoin (3, 10, 30 or 60 mg/kg) treatment and administered a 60 Hz corneal stimulation (25 mA). A 20 second max-out time was used for the mice that did not seize. Any seizure activity (i.e. clonic seizures defined as rapid spasms or jerky movements of the limbs) prior to tonic hindlimb seizure was recorded as presence of seizure.
All mice in the vehicle and Phenytoin 3 and 10 mg/kg groups displayed tonic seizure after a few seconds of receiving the current. Mice that were treated with Phenytoin 30 mg/kg all reached the 20 second timeout without displaying signs of a tonic seizure. Data are mean ± SEM, 20 second time-out; ***p<0.0001 compared to vehicle.
The MES model can be conducted in either rats or mice. Most studies can be completed as a one-day procedure. Group sizes are generally 8-12 animals.
Frequently Asked Questions
The endpoint most commonly used is the latency for seizure induction.
This test is a terminal test where animals are euthanized after the completion of the shock and seizure. However, animals are able to be utilized in other studies, such as inflammation assays or pain assay. Our scientists would be more than happy to tailor a study to minimize the number of animals needed without compromising data integrity.
This test can be run in rats or mice.
Synonyms: Epilepsy, MES, Seizures