Standard mHFD NASH Model
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome that can progress to liver cirrhosis. It afflicts as many as 12% of indiviuals in the U.S.[1] and is a leading reason for liver transplants.
Melior has established a NASH animal model with higher face validity qualities and that we believe is more clinically translatable than other popular models [2]. Our NASH model exhibits pronounced obesity, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, accompanied by liver steatosis, inflammation, fibrosis and hepatic triglyceride content [3]. In this way, we believe that this model closely mimics most features of human NASH and may represent the most relevant rodent model of NASH.
Importantly, we have validated this model with the PPAR alpha agonist fenofibrate, and the clinical proven NASH candidate, obeticholic acid (OCA; an FXR agonist).
Melior also has a variation of this model wherein the development of the fibrosis component of the disease is accelerated and more pronounced at a given age of the animals (see mHFD NASH Model with Enhanced Fibrosis)
Below are data comparing a standard diet (SD) with our modified diet (MD)-treated animals on vehicle, fenofibrate or OCA (N=9-12).
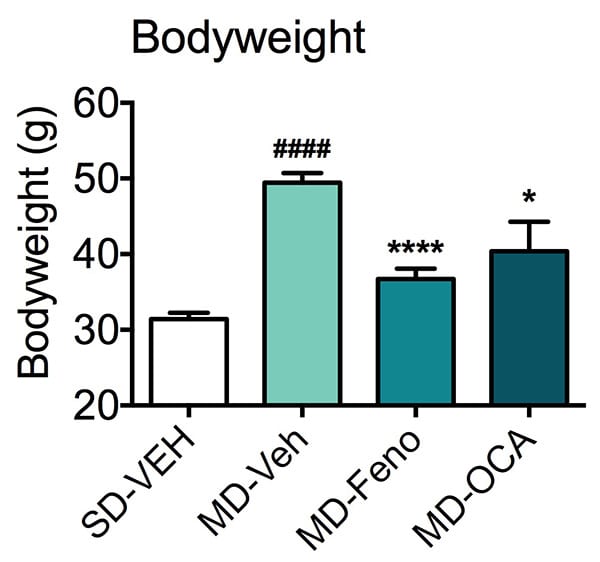
Bodyweight. Bodyweight at the end of the study was increased in the mice with the modified diet. This increase was significantly reduced by Fenofibrate and OCA. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by Unpaired T-tests as applicable (*p<0.05, ****p<0.0001, vs. MD-Vehicle; #### p<0.0001, vs. SD-Vehicle).
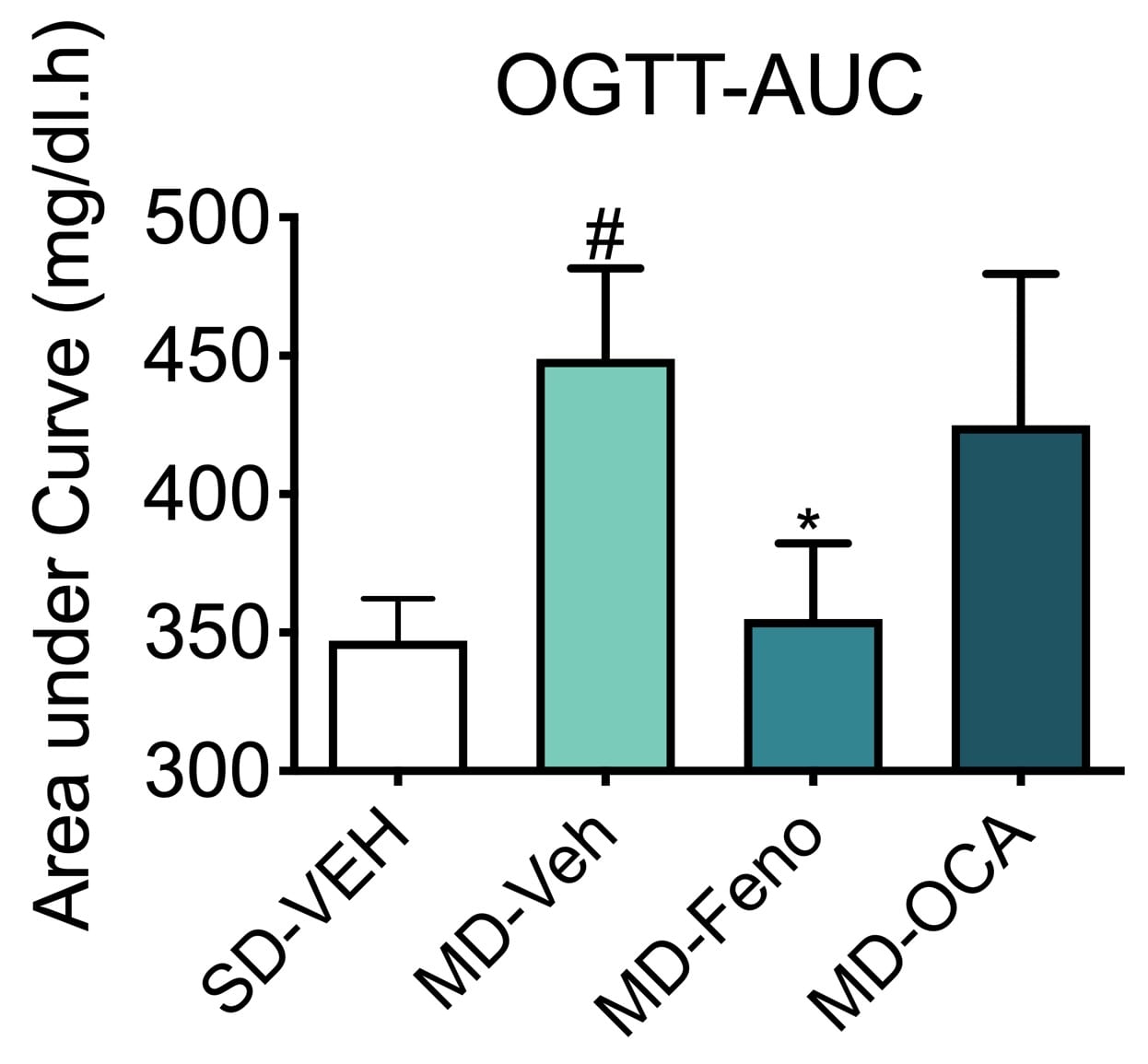 Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT). OGTT was performed after 6 weeks of compound treatment. Blood glucose was increased in the mice with the modified diet as seen in the area under the curve (AUC). This was significantly reduced by Fenofibrate. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by Unpaired T-tests as applicable (*p<0.05,**p<0.01,***p<0.001****p<0.0001, vs. MD-Vehicle; #p<0.05, ###p<0.001,#### p<0.0001, vs. SD-Vehicle).
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT). OGTT was performed after 6 weeks of compound treatment. Blood glucose was increased in the mice with the modified diet as seen in the area under the curve (AUC). This was significantly reduced by Fenofibrate. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by Unpaired T-tests as applicable (*p<0.05,**p<0.01,***p<0.001****p<0.0001, vs. MD-Vehicle; #p<0.05, ###p<0.001,#### p<0.0001, vs. SD-Vehicle).
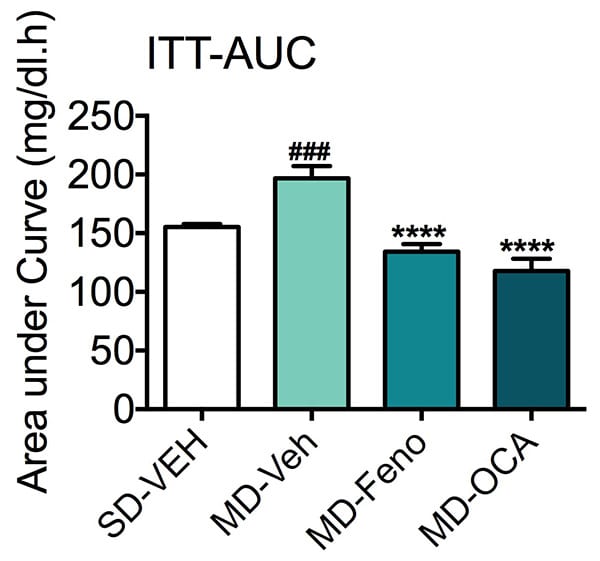
Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT). ITT was performed at week 8 of compound treatment to evaluate whole-body insulin sensitivity changes. Insulin resistance was increased in the modified diet mice as seen in the area under the curve (AUC). Both treatments significantly improved the insulin sensitivity. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by Unpaired T-tests as applicable (*p<0.05,**p<0.01,***p<0.001****p<0.0001, vs. MD-Vehicle; #p<0.05, ###p<0.001,#### p<0.0001, vs. SD-Vehicle).
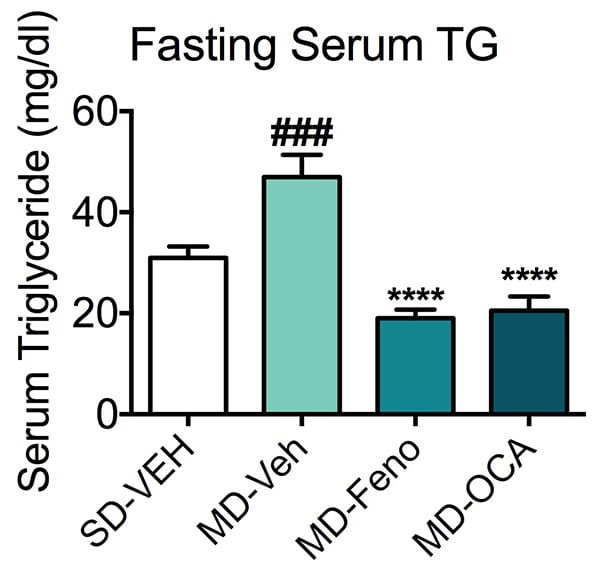
Serum Triglyceride (TG). Fasting serum TG were measured at the end of study. Serum TG was significantly increased in the mice with the modified diet. Fenofibrate and OCA significantly reduced these levels. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by Unpaired T-tests as applicable (**p<0.01,***p<0.001****p<0.0001, vs. MD-Vehicle; ###p<0.001,#### p<0.0001, vs. SD-Vehicle).
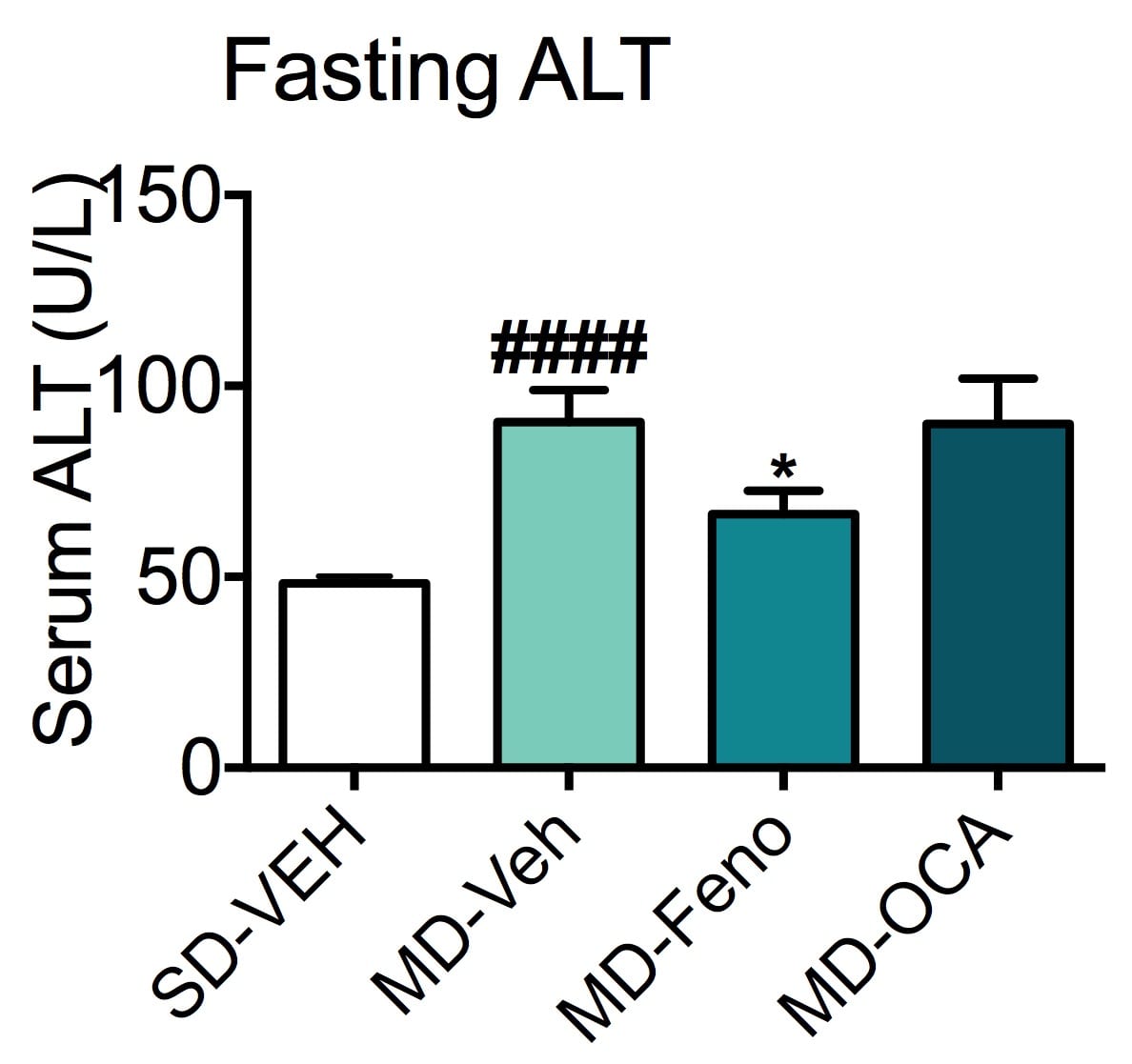
ALT level. Alanine Transaminase (ALT) is a commonly measured clinical biomarker of liver health. Fasting ALT levels were measured at the end of the study. ALT levels were significantly increased in the mice with modified diet. Fenofibrate significantly reduced these levels. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by Unpaired T-tests as applicable (*p<0.05vs. MD-Vehicle;#### p<0.0001, vs. SD-Vehicle).
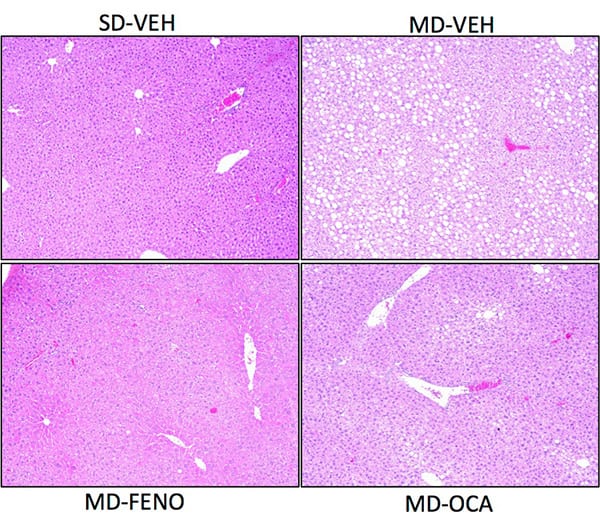
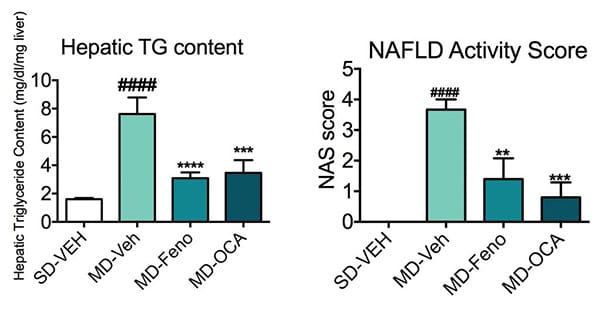
Hepatic TG and Histological Changes (NAS). Evaluations were made at the end of the study for Hepatic triglycerides (TG) and histology scoring through NAFLD activity score (NAS; [4]). Mice with the modified diet showed a significant increase in TG deposits in the liver and NAS. Fenofibrate and OCA significantly reduced both hepatic TG and NAS. Data are mean±SEM and analyzed by Unpaired T-tests as applicable (*p<0.05,**p<0.01,***p<0.001****p<0.0001, vs. MD-Vehicle; #p<0.05, ###p<0.001,#### p<0.0001, vs. SD-Vehicle).
Conclusion
Based upon these results, we conclude that the modified high fat diet model described here faithfully recapitulates most clinical aspect of NASH including; marked steatosis, fibrosis, obesity, marked insulin resistance and dyslipidemia. This NASH animal model is validated with OCA which is a compound that has been shown to show clinical efficacy towards NASH.
Reference
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash/definition-facts
- Saito, K, et al. Characterization of hepatic lipid profiles in a mouse model with nonalchoholic steatohepatitis and subsequent fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2015: 5:12466
- Cong WN, Tao RY, Tian JY, Liu GT, Ye F. The establishment of a novel nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model accompanied with obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Life Sciences 2008; 82:983–990
- Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Natta MV, Behling C, Contos MJ, et.al. Design and Validation of a Histological Scoring System for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology, 2005; 41:1313–1321