Morphine - Induced Constipation Assay
Discover how Melior’s unique phenotypic screening platforms can uncover the untapped value of your candidate therapeutic
This opioid induced constipation model is a method for evaluating a test compound’s ability to alter colonic propulsive motility. More specifically, this is a model that challenges animals with morphine to induce constipation.
This model is designed to identify pharmacological agents that can functionally antagonize or relieve the constipation produced by opioids, such as morphine, as measured by an increase in colonic propulsive activity. This model can be used to identify drugs that directly affect opioid receptors or that functionally affect opioid induced constipation.
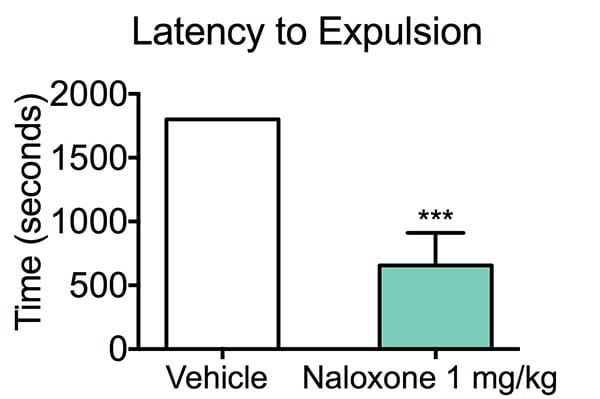
In this study, we tested the ability of Naloxone, a well-known mu-opioid receptor antagonist, on morphine-induced reductions in colonic propulsive activity (constipation).
Ready to get started or looking for a custom model?
Contact us today for more information about our bespoke research models and to discuss how we can help you answer your unique research questions.
Latency to Expulsion. Mice were treated with either vehicle or Naloxone 30 minutes prior to Morphine challenge. Mice were then administered Morphine 30 minutes prior to the colonic propulsion study. At peak drug time, a 3 mm glass bead was inserted through the anus into the distal colon. Mice were observed for the expulsion of the bead and the time noted, with a cutoff of 30 minutes. Naloxone, a well-known mu-opiod receptor antagonist, alleviated the time to colonic propulsion and constipation. Mice treated with vehicle had a significantly increased expulsion time compared to Naloxone-treated mice. Data are mean ±SEM; **p<0.01 compared to control mice (N=8).
- Like most gastrointestinal models, this model is typically performed in one day after a single administration of test article.
- It has relatively low variability and can generate statistically significant effects with group sizes of 6 to 8 animals.
- It can be used with both mice and rats.